TenJet
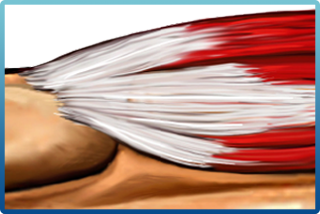
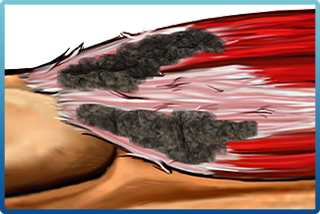
TenJet, a needle-like device meticulously designed for addressing tendinosis or chronic tendinitis, offers relief from persistent tendon pain. This innovative apparatus employs a pressurized, high-velocity jet of saline to precisely resect and eliminate damaged tendon tissue while safeguarding the integrity of healthy tissue.
In the realm of sports medicine, TenJet empowers physicians to treat individuals grappling with chronic tendon pain associated with conditions like Tennis Elbow, Golfers’ Elbow, Jumper’s knee, Achilles tendinosis, or tendon calcifications in the shoulder, elbow, hamstring, or hip. Furthermore, it proves effective in managing plantar fasciitis.
This minimally invasive tendon treatment necessitates only a small incision and is conducted in an outpatient setting. Real-time ultrasound imaging is utilized to visualize the diseased tissue, aligning with the objective of resecting diseased tissue akin to traditional open or arthroscopic surgeries.
What Is Tendinitis?
Tendinitis is characterized by inflammation of the tendon and is typically not associated with the degeneration or breakdown of tendon fibers.
What Causes Tendinitis?
The origins of tendinitis can vary among individuals. In certain instances, tendinitis and tendon inflammation may result from sudden injuries or strains during physical activity. Alternatively, repetitive motion injuries can lead to chronic tendinitis, also referred to as systemic tendinitis, creating a propensity for recurrent tendinitis or increased susceptibility in some individuals.
Where Do Patients Experience Tendinitis Pain?
Patients often encounter tendinitis pain in tendons prone to injury through repetitive strain or sports-related activities. Common instances include:
- Plantar Fasciitis in the foot
- Achilles’ tendon
- Patella or Quadriceps tendons in the knee
- Hip tendons such as the gluteus maximus, gluteus minimus, Ilio-tibial band, hamstring
- Extensor tendon in the elbow (tennis elbow or lateral epicondylitis)
- Flexor tendon in the elbow (golfers elbow or medial epicondylitis)
- Biceps tendon in the shoulder
- Rotator cuff tendons (supraspinatus and/or infraspinatus tendons) in the shoulder
How Is Tendinitis Diagnosed?
Tendinitis is typically diagnosed based on a patient’s clinical history and a physical examination conducted by a physician. Additional tests, such as MRI or ultrasound, may be employed in some cases to confirm that tendon pain results solely from inflammation, excluding other potential causes of pain.
Is Tendinitis Permanent? How Long Does Tendinitis Last?
Tendinitis is not a permanent condition. In the majority of cases, patients with tendon inflammation should experience healing within three months through conservative treatments.
How Is Tendinitis Treated?
Inflammatory tendinitis may resolve with rest and ice, and physicians may recommend bracing, corticosteroid injections, or physical therapy.
What Kind of Doctor Treats Tendinitis?
Typically, tendinitis is managed by orthopedic or sports medicine/interventional pain physicians. In certain situations, patients may be referred to physical therapy or other allied health specialists as needed.
Tendinitis vs. Tendinosis
The majority of tendon injuries can be classified into two categories: Tendinitis and tendinosis.
Tendinitis and tendinosis represent distinct types of tendon injuries. While tendinosis is commonly labeled as chronic tendinitis, distinguishing between the two can significantly influence your treatment plan and the time needed for resolution, as each necessitates unique approaches to treatment.
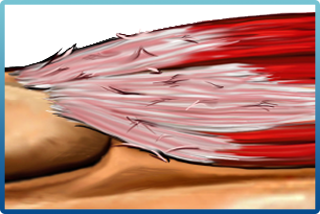
Tendon injuries may stem from a singular incident or activities characterized by repetitive motion, leading to micro-tears within the collagen fibers of the tendon.
| A robust tendon consists of resilient, flexible bands of connective tissue responsible for transmitting the energy required to facilitate movement from muscles to bones. Ligaments, like the plantar fascia, share a comparable structure and composition with tendons and are susceptible to injuries akin to those affecting tendons. | |
| Tendinitis is characterized by inflammation of a tendon, typically arising from an acute injury or strain on the tendon. This condition can lead to discomfort and sensitivity in the fibrous connective tissue located outside the joint, bridging the muscle and the bone. | |
| Tendinosis denotes a condition where a tendon experiences structural breakdown and exhibits disorganized collagen fibers. During this stage, tendons may retain fluid, form calcifications, and, without intervention, progress to partial or complete tears, with a potential risk of rupture. |
Frequently Asked Questions
- Will I experience pain during the procedure?
- Initially, you may encounter some discomfort as the physician administers a local anesthetic at the commencement of the procedure. Post-treatment, you might feel soreness in the treated area as the effects of the anesthetic subside.
- What is the expected duration of my recovery?
- On average, improvements in tendon pain may be noticeable as early as two weeks after the procedure, with substantial relief continuing within three months for those treated for chronic tendinitis or tendinosis. Your physician will outline a tailored post-treatment recovery plan, incorporating physical therapy and/or home exercises. Individual outcomes and the time required for complete symptom relief can vary based on adherence to post-procedure instructions and other influencing factors.
- Will stitches be necessary after my treatment?
- In cases where TenJet is utilized in a minimally invasive procedure, stitches may not be required.
- Is TenJet covered by insurance?
- Most insurance providers offer reimbursement for tendon treatment procedures, and your physician may use TenJet to perform the necessary procedure.