Ankle, Heel & Foot Pain
Stepping Out of Discomfort: A Comprehensive Guide to Ankle, Heel, and Foot Pain
Ankle, heel, and foot pain can be a hindrance to daily activities, affecting mobility and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the complexities surrounding pain in these areas, exploring the diverse causes, diagnostic approaches, and a range of treatment options, with a focus on advanced interventional modalities for effective relief.
Causes of Ankle, Heel, and Foot/Feet Pain:
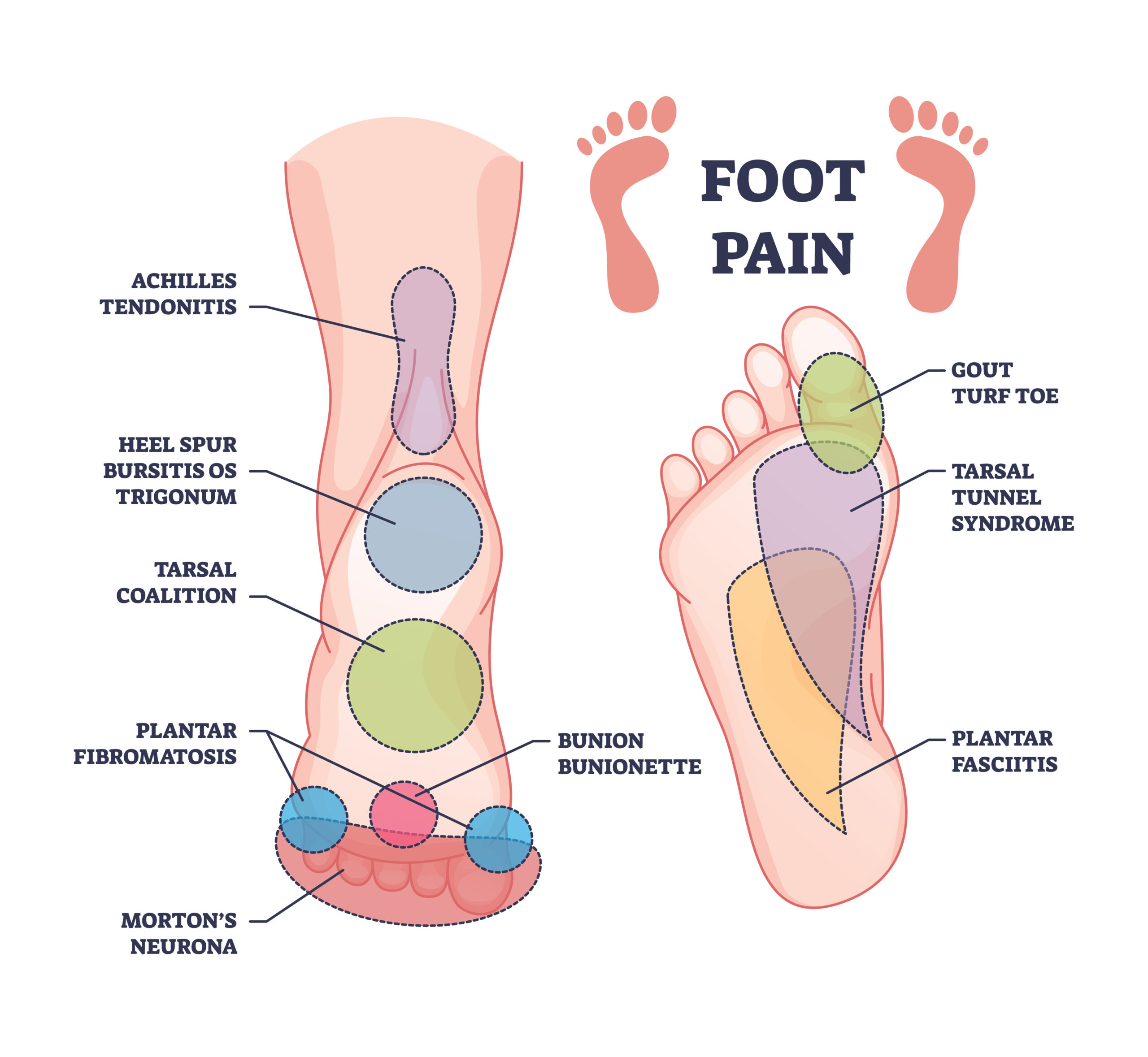 1. Plantar Fasciitis:
1. Plantar Fasciitis:
- Inflammation of the plantar fascia, a ligament supporting the arch of the foot.
2. Achilles Tendinitis:
- Inflammation of the Achilles tendon, commonly occurring in athletes.
3. Sprains and Strains:
- Ligament or muscle injuries resulting from overstretching or tearing.
4. Arthritis:
- Inflammatory joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
5. Neuropathy:
- Nerve damage leading to pain, tingling, or numbness in the foot.
6. Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Compression of the tibial nerve within the tarsal tunnel.
Examination and Tests to Diagnose a Cause:
1. Clinical Evaluation:
- Assessment of medical history, symptoms, and physical examination by a healthcare professional.
2. Imaging Studies:
- X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to visualize bones, joints, and soft tissues.
3. Blood Tests:
- To rule out systemic conditions like arthritis or diabetes.
4. Nerve Conduction Studies:
- Evaluating nerve function in cases of neuropathy.
Location of Pain Indicating a Possible Source:
1. Heel Pain:
- Common in plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendinitis, or heel spurs.
2. Arch Pain:
- Associated with conditions like flat feet or fallen arches.
3. Ankle Pain:
- Can stem from sprains, fractures, or arthritis.
4. Toe Pain:
- Often related to conditions like ingrown toenails or gout.
Treatment Options:
1. Rest and Ice:
- Initial management to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
2. Physical Therapy:
- Exercises to strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and correct gait issues.
3. Orthotics:
- Custom shoe inserts to provide support and alleviate pressure.
4. Medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain relievers for symptomatic relief.
5. Corticosteroid Injections:
- Targeted injections to reduce inflammation in cases of severe pain.
6. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- Regenerative approach using concentrated platelets to promote healing.
7. Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT):
- Application of shock waves to stimulate tissue repair.
8. Surgery:
- Reserved for severe cases, addressing issues like ligament tears or joint deformities.
Conclusion:
Ankle, heel, and foot pain, though disruptive, can be effectively managed through a tailored treatment plan that addresses the specific underlying cause. While conservative measures play a pivotal role, advanced interventional modalities like corticosteroid injections, PRP therapy, and shock wave therapy offer promising avenues for long-term relief. Consulting with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment ensures a comprehensive approach to stepping out of discomfort and reclaiming a pain-free stride.
References:
- Thomas, J. L., Christensen, J. C., & Kravitz, S. R. (2010). The diagnosis and treatment of heel pain: a clinical practice guideline-revision 2010. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery, 49(3 Suppl), S1–S19.
- Landorf, K. B., Menz, H. B., & Maher, C. G. (2010). Plantar heel pain and fasciitis. BMJ Clinical Evidence, 2010, 1111.
Further Reading:
- Goff, J. D., Crawford, R., & Christiansen, L. (2011). Foot and ankle conditions: plantar fasciitis. FP Essentials, 387, 11–20.
- Irving, D. B., Cook, J. L., & Young, M. A. (2007). Impact of chronic plantar heel pain on health-related quality of life. Journal of the American Podiatric Medical Association, 97(5), 339–347.