Percutaneous Discectomy
Dekompressor disc removal system
Stryker Dekompressor system helps relieve pain caused by contained disc herniations through a procedure called percutaneous discectomy. This minimally invasive procedure can measurably and selectively extract disc material without annular or nuclear disruption.
If you. are experiencing low back pain caused by a herniated disc, open surgery is one option. But disc decompression may be a treatment alternative.
Features/Benefits
Multiple clinical studies show that percutaneous discectomies using Stryker Dekompressor System are successful for 90% of patients. This minimally invasive procedure reduces pressure on the nerve root by removing disc nucleus.
-
- Significant pain relief
- Reduced use of pain medication
- Improved function for normal daily activities
- Defined amount of disc material removed
- Less scarring
- Quick recovery: 3-5 days, generally
- Low complication and morbidity rates
- Performed with local anesthesia as an outpatient procedure. Studies have shown a low rate of complications with percutaneous discectomy versus open surgery.
Indications
Minimally invasive percutaneous discectomy is used to treat sciatica caused by a contained disc herniation.
Procedure
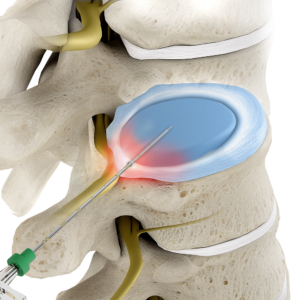
Percutaneous discectomy (sometimes called a Dekompressor discectomy because of the tools used) is a minimally invasive procedure used to reduce a herniated disc. The procedure uses a small needle to reach the disc, eliminating the need for an incision. The needle is guided to the disc by fluoroscopy (live x-ray) and a probe with a rotating tip is carefully inserted through the needle.
When the probe is turned on, its rotating tip removes small portions of the disc nucleus, creating empty space, allowing the disc to reabsorb the herniation and relieving pressure on the nerve. Because only enough of the disc is removed to reduce pressure inside the disc, the spine remains stable.
The procedure is usually reserved for patients who have not had success with conservative treatments like medications, physical therapy and nerve blocks. Typically, the patients are not candidates for surgery because the disc bulge is very small.
Credits & Sources: