Occipital Nerve Block
Occipital nerve Block (ONB)
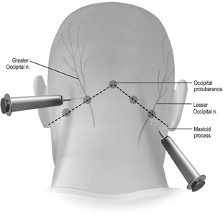
An occipital nerve block is an injection of medication that helps relieve posterior headaches known as occipital neuralgia. This type of headache starts from the base of skull on one side of head and may extend as far as the temple, forehead, and behind the eyes.
ONB is one of the most common procedures to provide pain relief for migraines and chronic headaches.
Indications
- Occipital neuralgia, an electric-like shooting, stinging, or burning pain at the back of head.
- Incision pain that can occur after surgery for Chiari, C1-C2 spine fusions, or a craniotomy at the back of the skull.
- Shingles of the scalp (post-herpetic neuralgia).
- Tension or cluster headaches.
What Are Occipital Nerves
 The greater occipital nerve is a spinal nerve, specifically the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve. This nerve arises between the first and second cervical vertebrae, along with the lesser occipital nerve. It ascends after emerging from below the suboccipital triangle beneath the obliquus capitis inferior muscle. It then passes through the semispinalis muscle before ascending to innervate the skin along the posterior part of the scalp to the vertex. It innervates the scalp at the top of the head, over the ear and over the parotid glands.
The greater occipital nerve is a spinal nerve, specifically the medial branch of the dorsal primary ramus of cervical spinal nerve. This nerve arises between the first and second cervical vertebrae, along with the lesser occipital nerve. It ascends after emerging from below the suboccipital triangle beneath the obliquus capitis inferior muscle. It then passes through the semispinalis muscle before ascending to innervate the skin along the posterior part of the scalp to the vertex. It innervates the scalp at the top of the head, over the ear and over the parotid glands.
Disorder of this nerve is one of the causes of cervicogenic headaches, referred to as occipital neuralgias. Occipital neuralgia can be the result of pinched nerves or muscle tightness in the neck. It can also be caused by a head or neck injury. Occipital neuralgia can either be primary or secondary. A secondary condition is associated with an underlying disease. Although any of the following may be causes of occipital neuralgia, many cases can be attributed to chronic neck tension or unknown origins.
- Osteoarthritis of the upper cervical spine
- Trauma to the greater and/or lesser occipital nerves
- Compression of the greater and/or lesser occipital nerves or C2 and/or C3 nerve roots from degenerative cervical spine changes
- Cervical disc disease
- Tumors affecting the C2 and C3 nerve roots
- Gout
- Diabetes
- Blood vessel inflammation
- Infection
Procedure
Steroid injections, with or without botulinum toxin, can “calm down” the overactive occipital nerves. This particular injection can be performed in the office, or in a ambulatory surgical facility, if you require sedation.
Risks and complications
- Bleeding or bruising at the needle insertion site
- Infection
- Nerve injury
- L Morris: Vol. 7, 197–203, April 2010
- Medscape
- HealthLine
- AANS
- Practical Neurology 2010: Procedural Treatments for Headache Disorders